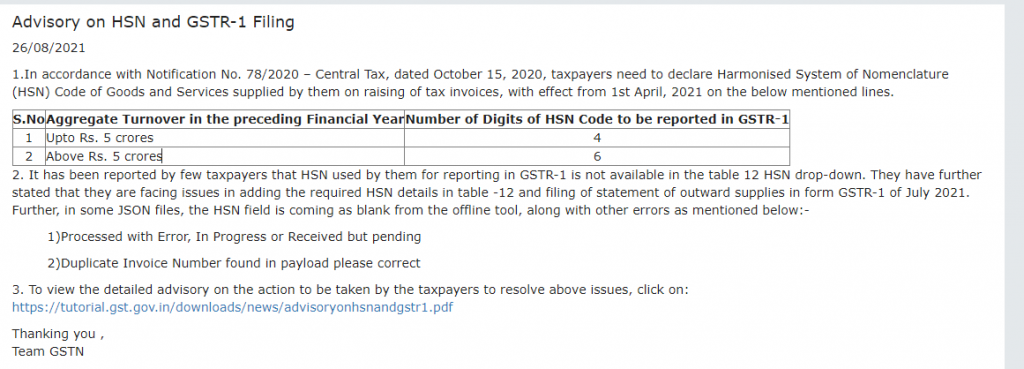
Every registered taxable person has to furnish outward supply details in Form GSTR-1 (GST Returns-1) by the 10th of the subsequent month. On the 11th, the visibility of inward supplies is made available to the recipient in the auto-populated GSTR-2A. The period from 11th to 15th will allow for any corrections (additions, modifications and deletion) in Form GSTR-2A and submission in Form GSTR-2 by 15th of the subsequent month.The corrections (addition, modification and deletion) by the recipient in Form GSTR-2 will be made available to supplier in Form GSTR-1A. The supplier has to accept or reject the adjustments made by the recipient. The Form GSTR-1 will be amended according to the extent of correction accepted by supplier.
On 20th, the auto-populated return GSTR-3 will be available for submission along with the payment. After the due date of filing the monthly return Form GSTR-3, the inward supplies will be matched with the outward supplies furnished by supplier, and then the final acceptance of input tax credit will be communicated in Form GST MIS-1.
Also, the mismatch input tax credit on account of excess claims or duplication claims will be communicated in Form GST MIS-1. Discrepancies not ratified will be added as output tax liability along with interest. However, within the prescribed time, if it is ratified, the recipient will be eligible to reduce this output tax liability.
Format Of Various GST Forms:-
Types of GST Returns to be filed by normal taxpayers
GSTR-1
The taxpayer records all his outward supplies of goods and services in details in this form. This has to be mandatorily done by the 10th of the next month. This will form the basis of all future flow and match for credit reconciliations. GSTR-1 is a detailed form containing 13 different heads. The critical headings are:
- GSTIN of the Taxable Person – Auto populated result
- Name – Auto populated result
- Gross Turnover in Last Financial Year – This has to be filed only once. From next year onwards, this field will be auto populated
- The Period for which the return is being filed – Month & Year shall be available as a drop down for selection
- Taxable outward supplies – Here, IGST shall be filled only in the case of inter-state movement whereas CGST and SGST shall be filled in case of intra-state movement. Moreover, details of any exempted sales or sale at nil rate of tax shall also be mentioned here
- Outward Supplies to end customer, where the value exceeds Rs. 2.5 lakhs – Other than mentioned, all such supplies are optional in nature
- Any other supplies not covered in above 2 sections
- Debit Notes or Credit Notes Details
- Amendments to the details of any outward supplies of previous periods – This does not covers any changes by way of debit/credit notes
- Exempted, Nil-Rated and Non-GST Supplies – This is a Non-GST section. When the details of exempted sales or nil-rated sales have already been mentioned anywhere above, then only Non-GST shall be filled up here
- Export Sales
- Tax Liability arising out of advance receipts
- Tax Paid.
GSTR-2A
It is available on the 11th of the next month for the recipients to see and validate the information therein. Recipients have time between 11th – 15th of the next month to change any information, delete or add, based on their books of accounts.
GSTR-2
This form is the culmination of all inward supplies of goods and services as approved by the recipient of the services. The due date is 15th of the next month. It is auto-populated with the details of GSTR-2A. GSTR-2 shall include the following heads:
- GSTIN of the Taxable Person – Auto populated result
- Name – Auto populated result
- The Period for which the return is being filed – Month & Year shall be available as a drop down for selection
- Details of all inward supplies – Auto populated with the details of GSTR-1. The taxable person can make any further addition or changes to the invoice here
- Changes to the inward supplies made for any previous period
- Import of Goods – Imports are treated as Inter-state supply and IGST shall be applicable on the same
- Import of Goods in earlier periods
- Services received from a person outside India (Import of Services)
- Import of Services in earlier periods
- Debit notes or Credit notes Details
- Amendments made to Debit or Credit notes of previous periods
- Inward supplies emanating from Unregistered persons
- Credits received from an Input Service Distributor – Auto populated from details of GSTR-6
- TDS credit from specified persons – Auto populated from details of GSTR-7
- TCS credit from E-Commerce operators – Auto populated from details of GSTR-8
- Input Tax Credit remaining to be taken against an invoice, from which initially a partial invoice was taken
- Reverse Charge tax liability
- Amendment to such reverse charge tax liability
- Tax Paid
- Input Tax Credit Reversals – A dropdown containing reasons for such reversals shall be made available
- Amendments to such Input Tax Credit Reversals
GSTR-1A
The form shall be auto-populated after filing of GSTR-2 on the 15th of the next month, having all the correct or changed information. The supplier shall have the choice to accept or reject the changes made by the recipient. Following such acceptance, the GSTR-1 shall be revised to such extent.
GSTR-3
This form is auto prepared by 20th of the next month. It will have the details of all outward as well as inward supplies of goods and services as furnished in GSTR-1 and GSTR-2. After considering both the details, GSTN will determine your input tax credit availability or the amount of tax payable.
It will have the following details:
- GSTIN of the Taxable Person – Auto populated result
- Name – Auto populated result
- Address of the person – Auto populated result
- The Period for which the return is being filed – Month & Year shall be available as a drop down for selection
- Total turnover
- Export Turnover
- Taxable Turnover
- Non-GST Turnover
- Nil Rated or Exempted Turnover
- Total Turnover (Sum of 1-4)
- Details of outward supplies
- Inter-state supply to end customers
- Intra-state supply to end customers
- Inter-state supply to registered persons
- Intra-state supply to registered persons
- Exports
- Amendments to Sales Invoices, Debit Notes and Credit Notes
- Tax liability on such outward supplies
- Details of inward supplies
- Inter-State received
- Intra-State received
- Imports
- Amendments to Purchase invoices, Debit Notes and Credit Notes
- Tax liability on such inward supplies
- Reversals of Input Tax Credit
- Total tax liability for the period
- TDS received for the period
- TCS received for the period
- ITC for the period
Apart from the above details, a Part B has to be filed containing the details of,
- Any taxes, interests, penalties or fees paid during the period
- Any refunds claimed during the period w.r.t. cash ledger
GSTR-9
This is the annual return, which the taxpayer has to file by 31st December of the coming financial year. It is nothing but the accumulation of all 12 monthly GSTR-3 of the taxpayer. It would also include the amount of tax paid during the year, including details of exports or imports.
Apart from the above forms, the Government shall serve those taxpayers who fail to furnish the returns on time, notice in Form GSTR-3A.
After the GSTR-3 is fully accepted for the month, then final input tax credit shall be communicated through form GST ITC-1. The details of ITC-1 has to be confirmed in due time to get the credit for that month. If the same is not done in due time, then it will disallow the credit for the month and will be computed as a tax liability for the month instead.
Returns to be filed by Composition Tax Payers
GSTR-4A
Similar to the GSTR-2A above, GSTR-4A is generated quarterly for composition scheme taxpayers. It has the details of the inward supplies as reported by suppliers in GSTR-1.
GSTR-4
With the auto-populated details of GSTR-4A, the taxpayer can furnish all his outward supplies here. The due date is 18th of the following month and has to be filed quarterly. It also contains the details of tax payable and payment of tax.
GSTR-9A
This is the annual return for all composition tax payers. It has to filed by 31st December of the coming financial year and includes all the quarterly returns filed by the composition tax payer.
Returns to be filed by Foreign Non-Resident Taxpayer
GSTR-5
This is a detailed form containing the particulars of outward supplies, imports, tax paid, input tax availed and remaining stock. This has to be filed monthly within 20th of the next month or if the registration is given up, then within 7 days of such surrender or expiry of registration.
Returns to be filed by an Input Service Distributor
GSTR-6A
This form will be generated by 11th of next month after the suppliers have filed their GSTR-1 on 10th of the next month. It will be auto-populated with the details of inward supplier made to them. It has to be filed on a monthly basis by the ISD.
GSTR-6
Once the details are confirmed or corrected by the ISD, then GSTR-6 will be generated. It has to be filed by the ISD by 13th of the next month. This is also a monthly filing.
Returns to be filed by a Tax Deductor
GSTR-7
Details of the tax deductions made during the month has to be furnished here. The due date is 10th of the next month.
GSTR-7A
This is a TDS certificate, which is auto-generated upon filing the GSTR-7 by the tax Deductor. It will be available for the assessees to download and keep record of. It will contain details of the tax deducted and the total amount of payment made.
Return to be filed by an E-Commerce Portal
GSTR-8
This return shall contain all the supplies made by the E-Commerce seller and the amount of tax collected as well. It has to be filed by 10th of the next month.
For those assessees whose annual turnover exceeds INR 1 Crore, then a reconciliation statement in Form GSTR-9B has to be filed by 31st December of the next fiscal year. It has to be filed annually and is basically an audited annual accounts, duly certified by competent authority.
Where the assessee is a Government body or a United Nations Body, then a monthly Form GSTR-11 has to be filed by 28thof the next month. These bodies have a UIN (Unique Identification Number) and hence will be required to furnish the details of inward supplies.
Where a taxable person’s registration has been surrendered or cancelled, then a final return in Form GSTR-10 has to be filed within 3 months of such cancellation or registration. It will declare the input tax credit and capital goods held by the taxpayer, tax payable and paid at such time.
The Government has automated all the forms together by bringing the same details on a real time basis in front of the taxpayers. The step, which is of paramount importance, is Step No. 1, i.e. FORM GSTR-1. It will form the basis of all further activities.
Any shortcomings or short filings of information in the details provided by the suppliers can be rectified, changed or deleted by the recipients in ample period of time. It is a seamless process that matches all information together to get the final credit figures and tax payable, if any.
The payment challans are also a very crucial part of all the filing process. Without them, it is not possible to clear tax payments and dues in due course of time and also claim credit.
- PMT-1: An online tax liability register arising out of return or non-return related liabilities of the taxpayer.
- PMT-2: Credit balance online as in GSTN
- PMT-2A: Re-credit addition to the GSTN balance of a taxpayer
- PMT-3: Online cash ledger
Note: The above forms are maintained free of cost by the GSTN for each taxpayer. It can be accessed anytime through a User ID and Password, 24X7.
- PMT-4: Challan for payment of GST
- PMT-5: Payment register for unregistered taxpayers
- PMT-6: Application for claiming missing credit
Where it is found that there is an excess credit available in the account of a taxpayer, then the taxpayer has an option to claim refund of such excess credit within prescribed time. The refund application forms are different for the State and Central Governments.
There are 10 forms prescribed for the Central Government, out of which only 5 are applicable for the State application. The main form is RFD-01 where the application for refund is made.
GSTR 3B Return
In order to ease the burden on tax payers, tax authorities have introduced a simple return form called as GSTR 3B. This has to be used only for the december . Every registered tax payer (Except for composition scheme) needs to file a separate GSTR 3B for each GSTIN they have.
This is more like a self-declaration return and the tax payer is not required to provide invoice level information in this form. Only total values for each field have to be provided.
Due date for filing GSTR 3B return for July was 20th of the relavent month.